Space contains countless celestial bodies which travel without drawing attention from the people on Earth.
The scientific community shows interest in certain space objects when they approach close to Earth.
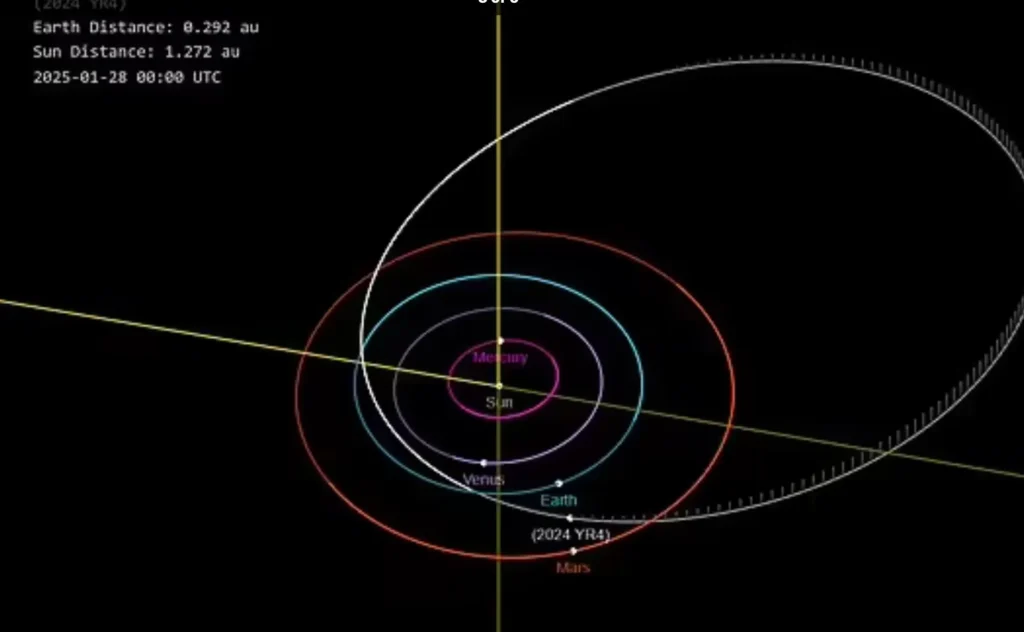
The scientific community has made a new asteroid discovered recently their primary area of interest and research focus.
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) telescope located in Río Hurtado, Chile made a new near-Earth object detection on December 27, 2024.
Scientists evaluate the diameter of asteroid 2024 YR4 at 40 to 100 meters corresponding to 130 to 330 feet.
Similar to the asteroid responsible for the Tunguska explosion in 1908 which leveled Siberian forest this object is of equivalent size.

Automated asteroid warning systems processed a complete trajectory report of 2024 YR4 after discovering the asteroid.
The initial trajectory assessments suggested 2024 YR4 may get near to Earth during its December 22, 2032 flyby.
At first glance such near space encounters appear safe because space is vast however the preliminary findings indicated a distant possibility that scientists wanted to assess further.
The European Space Agency (ESA) currently tracks this asteroid with great attention.
The recent studies from January 29, 2025 establish that 2024 YR4 demonstrates a 99% probability to safely bypass Earth in January 2024.
The analysts state that they maintain reservation about the total elimination of the potential for a collision.
Initial orbital observations usually produce high margins of error because of the lack of certainty in early predictions.
The United Nations has activated two international asteroid response groups that received their endorsement.
The International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN) jointly with the Space Mission Planning Advisory Group (SMPAG) work together to monitor and assess and when needed reduce the 2024 YR4 threat.
The advancement of asteroid survey technology leads to discovering a record number of space objects that approach Earth.
Improved detection capabilities allow us to identify more space objects although the actual threat environment might not have changed.
The discovery of numerous asteroids during initial observations has resulted in decreased probabilities when scientists obtain additional data.
Asteroid 99942 Apophis was originally considered dangerous to Earth during its 2029 approach.
Studies following the first observation eliminated any potential collision risk along that particular trajectory.
The Torino Impact Hazard Scale rates 2024 YR4 as Level 3 at the present moment.
Astronomers and public need to monitor this asteroid based on its Level 3 rating.
Research and analysis of this asteroid should persist because immediate concern is unnecessary.
Studies show that scientists want people to avoid reaching premature conclusions from initial data findings.
Predictions regarding the orbit of 2024 YR4 will improve after scientists acquire additional observational data.
International collaboration serves to properly evaluate any potential threat to Earth while implementing necessary protective measures.
All speculation and uncertainty aside there is one fundamental point that still stands true.
Scientific experts at present verify that asteroid 2024 YR4 possesses a 1.2 percent likelihood of striking Earth’s surface during its predicted December 22, 2032 approach.
Any strike of 2024 YR4 against Earth could create massive destruction focused on crowded urban areas.

The asteroid presents a risk of exploding in mid-air similar to the Tunguska event to create a devastating fireball along with a powerful shockwave.
The asteroid poses the risk of surviving its descent until it hits the surface and causes substantial damage by creating a big crater.
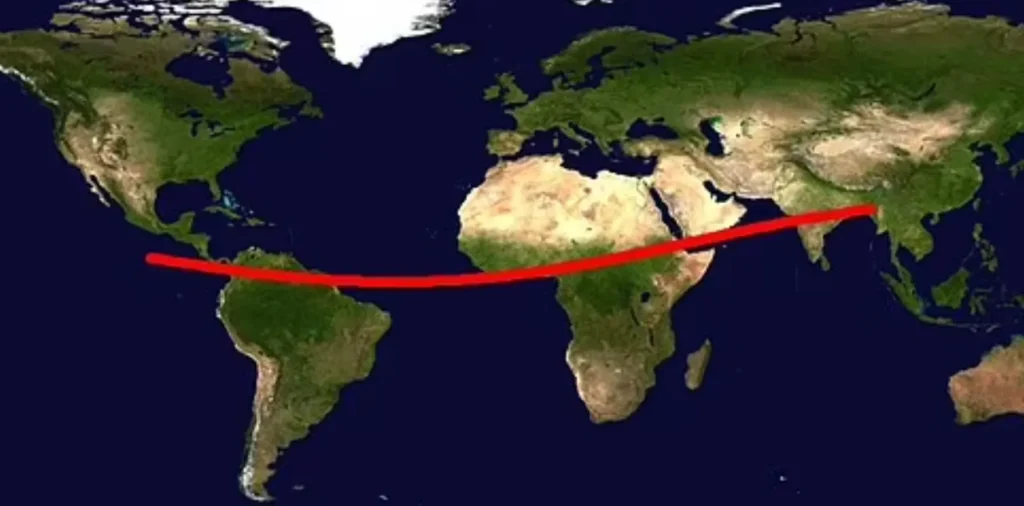
The current risk corridor—the likely impact region—stretches from South America across the Atlantic to sub-Saharan Africa.
The delineated impact zone needs constant updates with newly processed data.
Scientists work around the clock to collect data as they have only eight years until 2024 YR4 reaches its shortest point of approach to Earth.

Science has yet to determine many aspects about this asteroid as it travels through space at millions of miles distance.
The future of Earth depends heavily on what will happen during the next few years leading up to December 22, 2032.
Feature Image Credit: (NASA)

